Locally Advanced Breast Cancer
What is Locally Advanced Breast Cancer ( LABC)?
- Locally advanced breast cancer means that the breast cancer is quite large in size and has spread to the adjoining lymph nodes, muscles or skin. It has however not spread to the other sites in our body such as the lungs, liver or the brain. This is the most common presentation of women in India.
Is this LABC survivable?
- With modern treatment options many patients do well and survive for a long period of time.
How are patients with LABC diagnosed?
- Patients with LABC are diagnosed the same way as any other breast cancer is diagnosed. After clinical examination,the breast cancer is diagnosed by a Tru-cut biopsy. If there is an enlarged lymph node involved FNAC of the involved lymph node is then done. To know the extent of spread, a mammogram is done for the opposite breast, CT chest is done for the chest, Ultrasound abdomen is done for the abdomen and if necessary CT brain is done to know the extent of spread to the brain.
How is LABC treated?
- To contain the spread of the tumour and to make it smaller, patients with LABC are treated with chemotherapy. The medical oncologist decides upon the chemotherapy regimen that you need to take and the number of cycles depending upon the biopsy report and the general condition of the patient. This is called neoadjuvant chemotherapy wherein the chemotherapy is done before the surgery. After finishing chemotherapy, surgery is done to remove the breast cancer and reconstruction can be done in the same operation as that of the removal of the breast. The patient would then need radiotherapy after the removal of the cancer. Depending upon the presence of the endocrine receptors, hormone therapy is started after completion of radiotherapy.
What is the surgery done for LABC ?
- Surgery for LABC is divided into
- Surgery for the breast
- Surgery for the axilla
- Reconstruction of the breast
- The surgeon will examine the patient and will discuss with the patient regarding the correct procedure to be done for the patient.
- Surgery for the breast
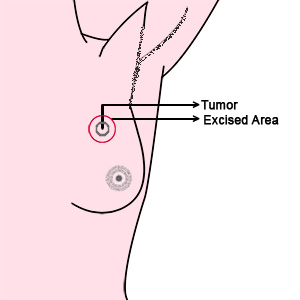
Breast Conservative Therapy (BCT)
- After neoadjuvant chemotherapy if the size of the tumour has reduced considerably and if the breast also does not have any other lesions such as DCIS or other tumours, then the breast lump alone can be removed with a small margin of normal tissue. The patient would definitely need radiotherapy after this procedure.
Mastectomy
- When the lump is large and when there are multifocal tumours elsewhere in the same breast, it is better to undergo removal of the breast entirely. After removal of the breast, it is recommended that women prefer to undergo reconstruction of the breast at the same time. Many women may not want breast reconstruction and they can opt to get it done later if they want.
- Surgery for the axilla
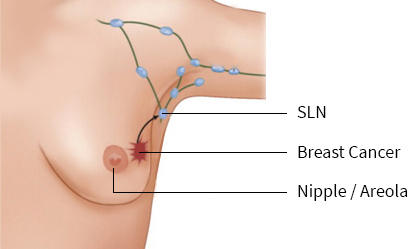
Sentinel Lymph node biopsy
- Sentinel lymph node is the first node that drains the tumour in the axilla. We inject the dye near the nipple and look for the first lymph node that it drains. We send this sentinel lymph node for biopsy and look out for the presence of any spread of tumour. If there is any infiltration of the lymph node by the tumour, then the patient would need a full axillary dissection.
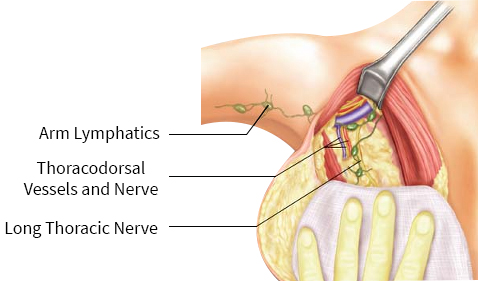
Axillary Lymph Node Dissection
- In this operation most of the lymph nodes in the axilla are removed.
Reconstruction of the breast
- Most patients undergo mastectomy or removal of the breast. This is because of the large tumour size and multifocal tumours. Breasts can be reconstructed from the same time. As patients with LABC usually need radiotherapy, patients would need reconstruction with thepatient’s own tissues. There are several methods of breast reconstruction of which DIEP ( Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator) flap is considered the gold standard means of reconstruction. Here the skin and fat below the umbilicus is taken along with the blood vessel that supplies it and is connected to the blood vessel in the chest or axilla by microsurgery and this is shaped to form a new breast




