ABOUT
Synovitis is Painful and swollen joints due to inflammatory conditions and due to arthritis of the knee.
Cause: The cause of the swelling and pain is usually inflammation and excessive growth of the synovium(tissue that lines the inside of a joint).
Normal synovium: A normal synovium, which is usually one or two cell layers thick, produces synovial fluid that helps to lubricate the joint.
Synovitis: Excessive proliferation of the synovium due to any underlying disorder like infection, inflammatory disorders like Rheumatoid arthritis can produce excessive fluid stretching the capsule causing pain and restricted movement. Depending on the cause and duration synovitis can be treated medically or surgically.
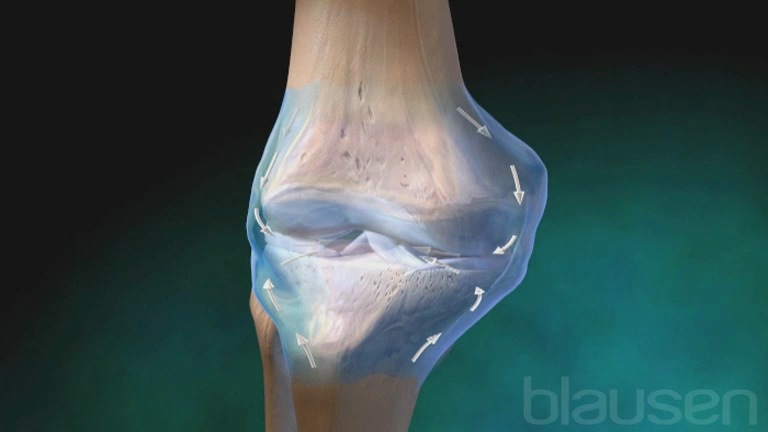
Figure: Normal synovial sheath with synovial fluid of the knee joint
SYMPTOMS AND INVESTIGATIONS
The classical symptoms of synovitis include joint
- pain,
- swelling,
- morning stiffness,
- difficulty in movement - stiffness of joints
- Deformities in the late stage.
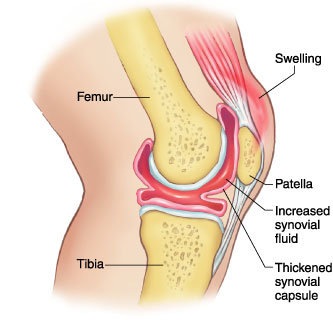
Figure: Pictorial illustration of the synovitis of the knee joint
Investigations would include a blood work up:
- complete blood count(CBC) ,
- C reactive protein (CRP) ,
- ESR(Erythrocyte sedimentation rate),
- Uric acid &
- rheumatoid factor
These investigations grading the magnitude of inflammation & can point toward the possible underlying cause
Radiological investigations like X rays and MRI of concerned joints would give an idea of the damage to joint cartilage and extent of inflammation.
TREATMENT CONSIDERATIONS
This includes a trial of DMARD’s (Disease modifying anti-rheumatoid drugs) in case of rheumatoid arthritis while there is no role for non-operative treatment in cases of suspected infection.
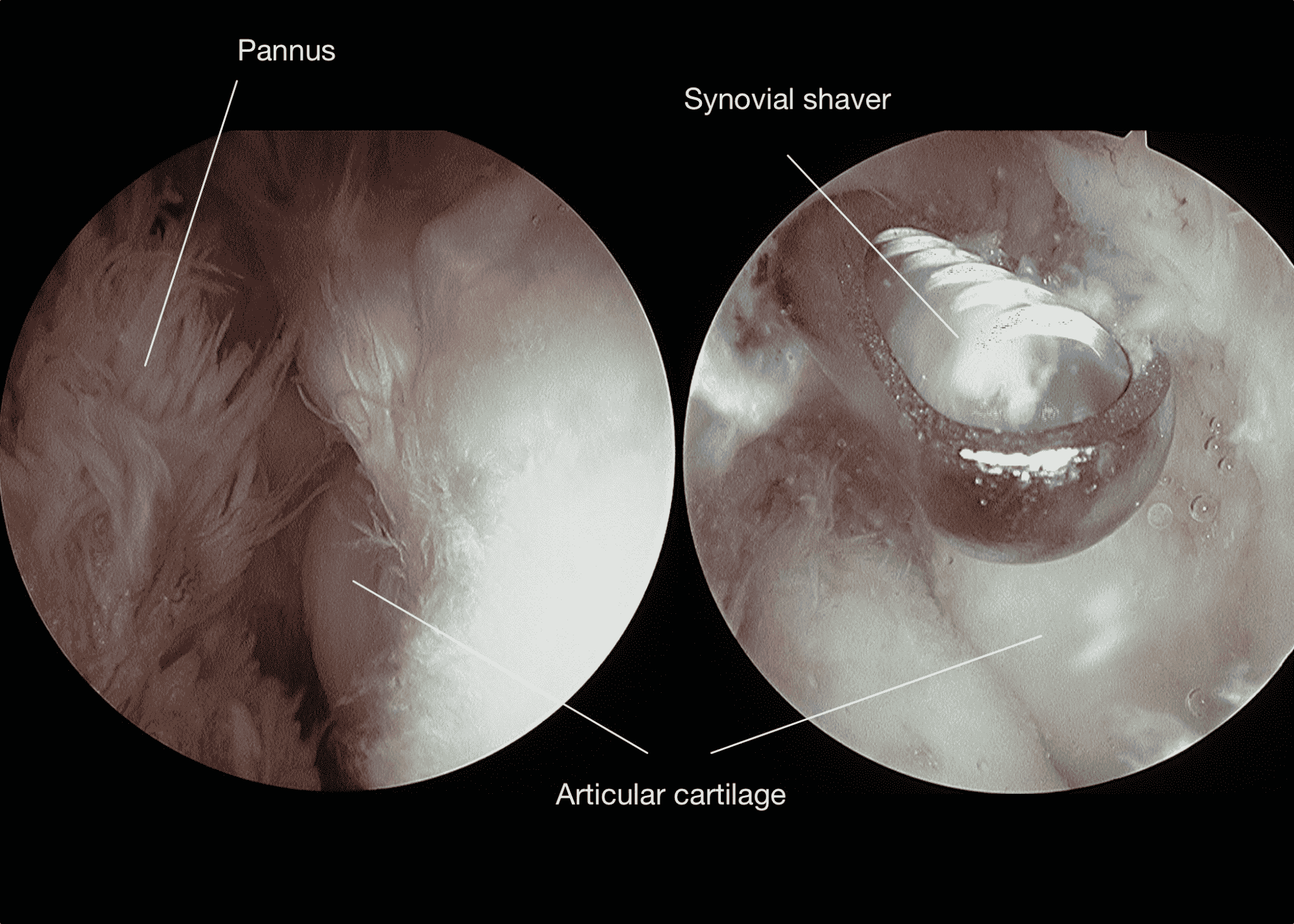
This includes clearing of the affected synovium using keyhole surgery-Arthroscopic synovectomy.
A sample of the tissue can be sent for biopsy and histopathological examination for a conclusive diagnosis.
In case of extensive cartilage damage due to long standing synovitis, Joint replacement maybe necessary.