About
The meniscus is a C-shaped piece of fibrocartilaginous structure in the knee that cushions and acts as a shock absorber between thigh bone (femur) and leg bone (tibia). There are two menisci: an inner (medial) and outer (lateral) meniscus that help to distribute the forces in the knee during weight bearing.
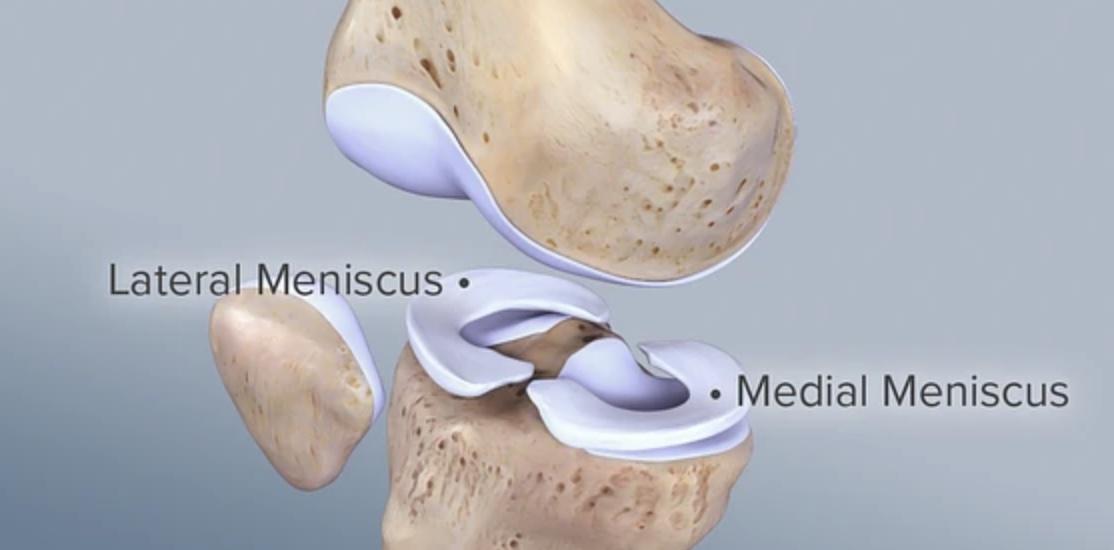
Meniscus can tear during any activity that involves twisting of the knee & can be associated with other ligament injuries within the knee joint. Sometimes meniscal root tears can occur due to degeneration & ageing process.
Outer one third of each meniscus has a rich blood supply & heals very well. Inner two third lacks blood supply. Hence the meniscal repairs are indicated for outer zone tears/red-red zone tears while meniscal trimming(partial meniscectomy) is indicated for inner zone tears/white-white zone tears.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Most common symptoms of meniscal injury include -
- Pain on walking,
- squatting,
- Catching or locking and
- Inability to move knee through its full range of motion.
On examination there may be tenderness on palpation. Pain and clicks on moving the knee into certain positions.
Investigation
Plain x-rays are of limited use in diagnosing meniscal injury, but they are taken to rule out any associated bony injuries.
MRI is used to diagnose and classify meniscal injuries.
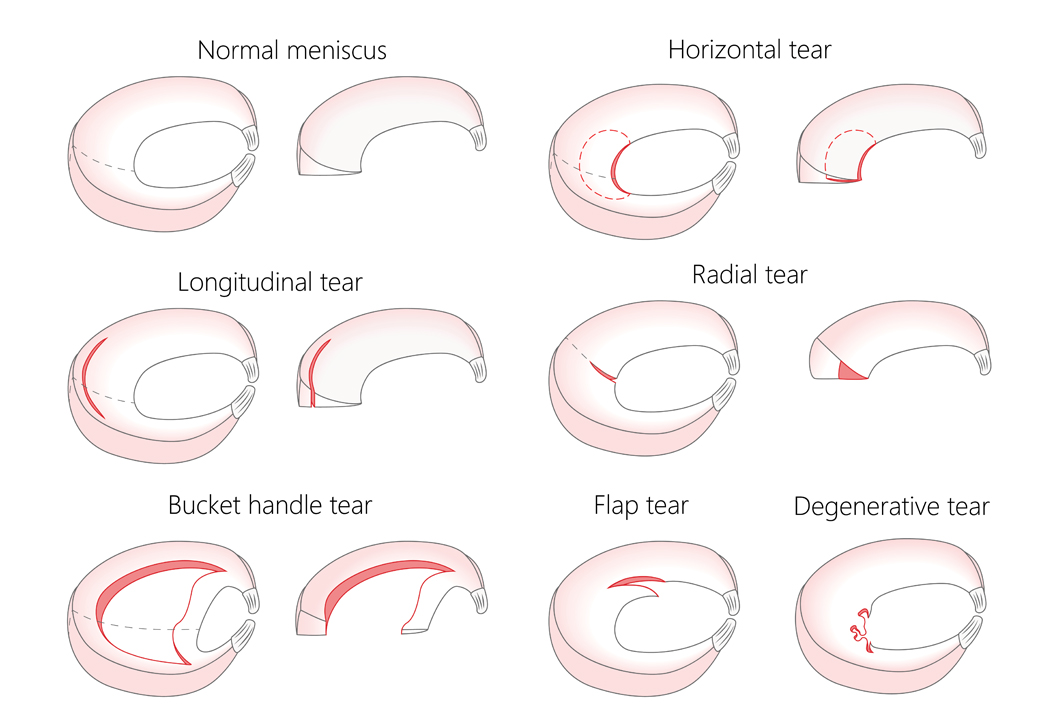
Type of meniscal tears
There are 6 types of tears based on the tear morphology - that is location of tear within the meniscus. Figure below illustrates all the types of tears.
TREATMENT
Meniscus plays an important role in load transmission. Untreated meniscus injury can lead to early arthritis of the knee joint. Preserving the meniscal structure and hence its functions is the intention of treating meniscal injuries.
Non surgical treatment includes restriction of squatting, cross legged sitting especially for isolated tears small tears which are due to gradual wear and tear due to ageing(degenerative tears)
SURGERY
Surgery is indicated for flap tears, large tears, bucket handle tears, radial and root tears. It includes arthroscopic meniscal repair and partial meniscectomy depending on the zone of involvement and morphology of tear.
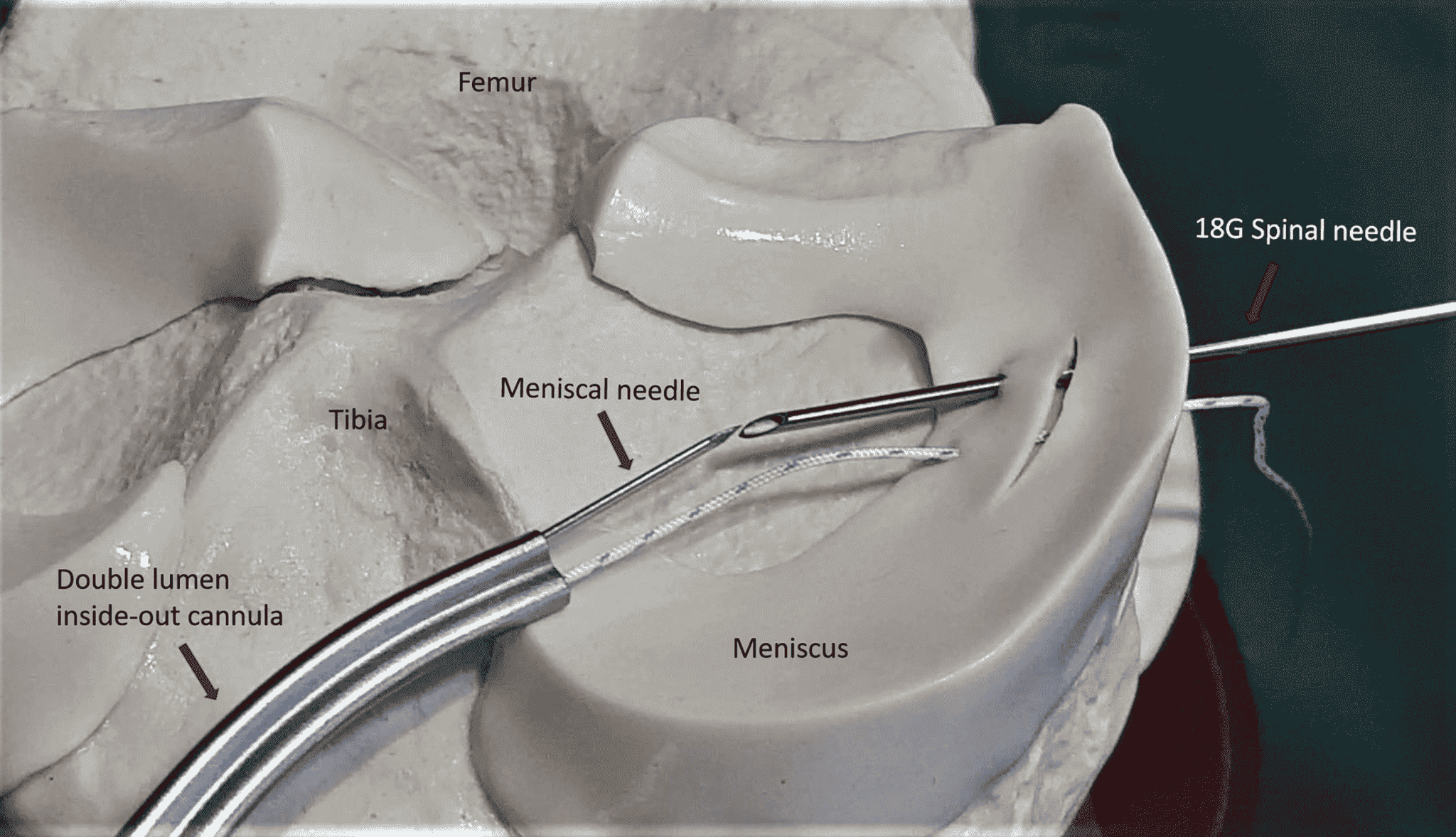
Figure: Showing insertion of needle and fibre wire(suture material) repair of meniscal tissue inside the knee joint.
Surgery is advisable for meniscal root tears & if meniscal tears are associated with cysts without a conservative trialAssociated ligament injuries are also addressed at the same time.
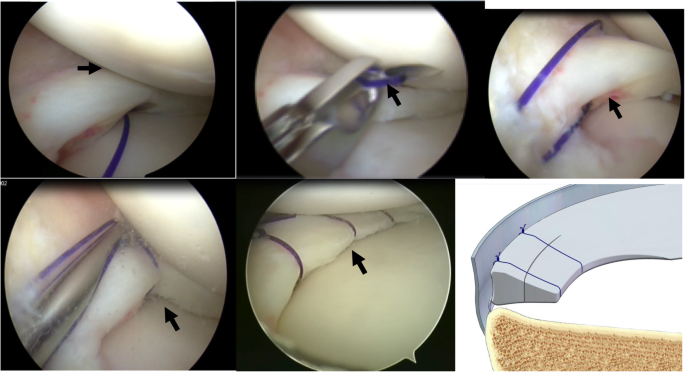
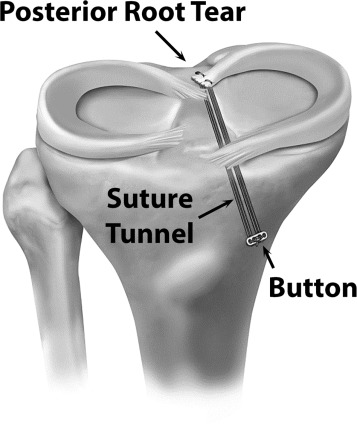
Figure: Arthroscopic meniscal repair and root repair




