DISTAL FEMUR AND PROXIMAL TIBIA FRACTURES: FRACTURES OF THE KNEE JOINT
Distal femur fractures and tibial plateau fractures are most commonly fractures following high-energy trauma, such as a fall from height or a road traffic accident.
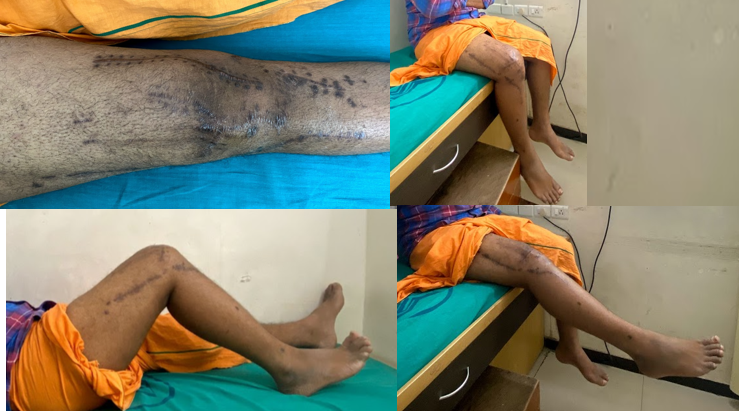
Patients will present with sudden onset pain in the affected knee, being unable to weight-bear, and associated with swelling of the knee. On examination, significant swelling will be evident, alongside tenderness over the medial or lateral aspects of the proximal tibia, with potential ligament instability.
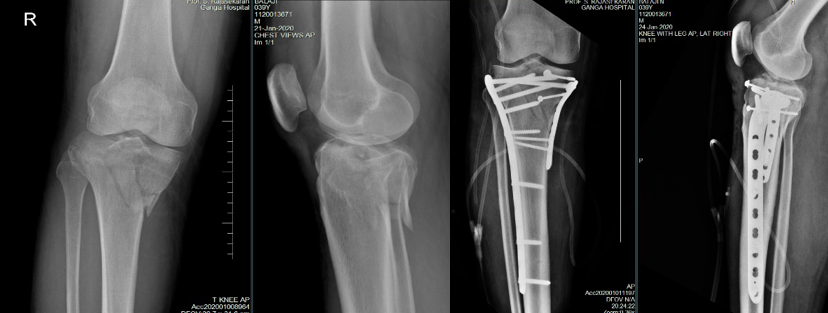
Distal Femur Fracture Fixed With Locking Plates

Proximal Tibia Bicondylar Locking Plate Fixation
Treatment
Non operative management can be attempted in uncomplicated Proximal tibia and Distal femur fractures
Operative management is warranted in Complicated Tibial condyle and Distal femur fractures with evidence of Compartment syndrome/ Bleeding wounds and treatment include Plate / Screw fixation of the Distal femur and Proximal tibia
Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) are the mainstay of these fractures, with the aim to restore the joint surface congruence and ensure joint stability. Any metaphyseal gaps can be filled with bone graft or bone substitutes.
OUTCOME